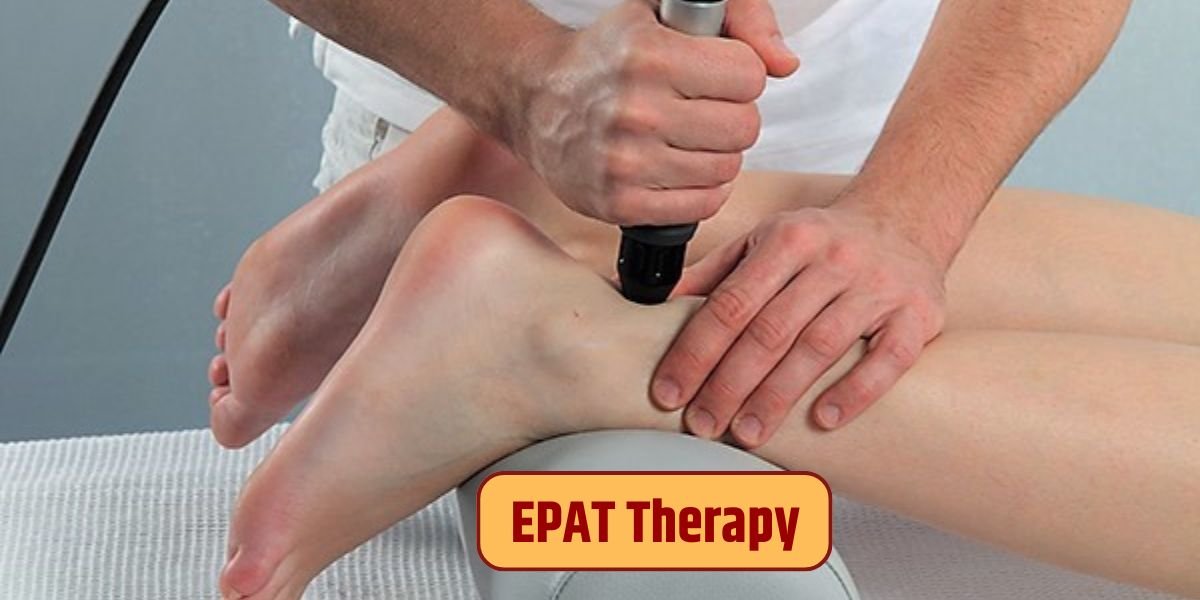
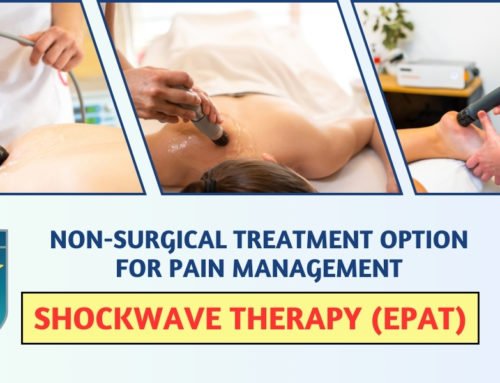
EPAT therapy, also known as Extracorporeal Pulse Activation Therapy, is a cutting-edge treatment option gaining popularity in the realm of musculoskeletal disorders. It utilizes the power of shockwaves to stimulate the body’s natural healing processes and alleviate pain. In this article, we delve into the intricacies of EPAT therapy, exploring its mechanism, effectiveness, and benefits.
Understanding Shockwave Therapy
Before delving into EPAT therapy, it’s essential to grasp the concept of shockwave therapy. Shockwave therapy involves the application of high-energy acoustic waves to affected areas of the body. These waves penetrate deep into tissues, promoting cellular regeneration and enhancing blood circulation.
How Does Shockwave Therapy Work?
Shockwaves are generated using a specialized device and directed towards the target area of the body. Upon contact with tissues, these waves stimulate the release of biological factors responsible for tissue repair and regeneration. Additionally, shockwaves help break down scar tissue and calcifications, facilitating the healing process.
EPAT Therapy Explained
EPAT therapy is a specific form of shockwave therapy designed to address various musculoskeletal conditions effectively. Let’s delve into what EPAT entails and how it works.
What is EPAT?
EPAT, or Extracorporeal Pulse Activation Therapy, involves the application of acoustic pressure waves to targeted areas of the body. These waves are delivered using a handheld device, allowing for precise localization and treatment.
Mechanism of EPAT Therapy
During an EPAT session, the device emits controlled pulses of acoustic energy, which penetrate deep into the affected tissues. These pulses trigger microtrauma at the cellular level, stimulating the body’s natural healing response. As a result, blood flow to the area increases, promoting tissue regeneration and pain relief.
Conditions Treated with EPAT Therapy
EPAT therapy has shown promising results in treating a wide range of musculoskeletal disorders. Some common conditions addressed by EPAT include:
- Plantar Fasciitis – EPAT therapy can help alleviate heel pain and inflammation associated with plantar fasciitis.
- Tendinitis – EPAT is effective in treating various forms of tendinitis, including Achilles tendinitis and tennis elbow.
- Musculoskeletal Disorders – EPAT therapy can be beneficial for conditions such as bursitis, fasciitis, and myofascial pain syndrome.
Benefits of EPAT Therapy
EPAT therapy offers several advantages over traditional treatment modalities:
- Non-invasive Treatment Option – Unlike surgery or injections, EPAT therapy is non-invasive and does not require anesthesia, reducing the risk of complications.
- Reduced Recovery Time – EPAT therapy typically requires minimal downtime, allowing patients to resume their daily activities shortly after treatment.
- Improved Mobility and Functionality – By promoting tissue regeneration and reducing pain, EPAT therapy helps improve overall mobility and functionality.
EPAT Therapy Procedure
The EPAT therapy procedure typically involves the following steps:
- Preparation – The patient is positioned comfortably, and the treatment area is cleaned and prepared.
- Administration – The EPAT device is applied to the target area, and controlled pulses of acoustic energy are delivered.
- Post-treatment Care – Following the session, patients may experience mild soreness or discomfort, which usually subsides within a few days. It’s essential to follow any post-treatment instructions provided by the healthcare provider.
Risks and Side Effects
While EPAT therapy is generally safe, some potential risks and side effects may occur:
- Common Side Effects – Mild soreness, bruising, or redness at the treatment site are common side effects that typically resolve within a few days.
- Who Should Avoid EPAT Therapy? – Individuals with certain medical conditions, such as pregnancy, cancer, or severe circulation disorders, may not be suitable candidates for EPAT therapy.
EPAT therapy offers a promising alternative for individuals suffering from musculoskeletal disorders. With its non-invasive nature, minimal side effects, and significant clinical evidence supporting its effectiveness, EPAT has become a preferred treatment option for many patients seeking relief from pain and improved function.
Consult Dr. Vikram Rajguru at The Prolotherapy Clinic, your trusted destination for athletes, chronic pain sufferers, and those seeking musculoskeletal relief.”
FAQs
- Is EPAT therapy painful?
- While some patients may experience mild discomfort during EPAT treatment, it is generally well-tolerated and minimally invasive.
- How many EPAT sessions are typically needed?
- The number of EPAT sessions required varies depending on the condition being treated and individual patient response. Typically, a series of 3-5 sessions spaced one to two weeks apart is recommended.
- Is EPAT therapy suitable for all types of musculoskeletal conditions?
- EPAT therapy has shown efficacy in treating various musculoskeletal conditions, but suitability should be assessed on a case-by-case basis by a qualified healthcare provider.
- How soon can I expect to see results from EPAT therapy?
- Some patients may experience immediate pain relief following the first EPAT session, while others may notice gradual improvement over several weeks.