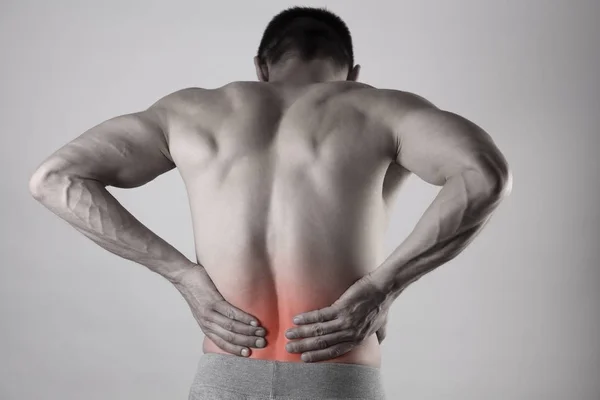
Any discomfort felt in the chest area is referred to as thoracic back pain. The thoracic spine may be found predominantly between the shoulder blades in the middle of the back of the chest (thorax). It stretches from the lower back (or neck) to the lower back (or lumbar spine), at or near the level of the waist.
Prevalence of Thoracic Back Pain
Researchers were asked to find out how many people got back pain and came back with the answer between 4 and 72 people out of 100. After hearing such accurate predictions, political pollsters quickly enlisted the researchers to do the same for the next midterm elections.
The fact is that if various polls aren’t given the same question, they will get different results. It is well-documented that adolescent women are more vulnerable to thoracic back discomfort.
Who is affected by this condition?
The findings of polls asking how many individuals have discomfort in their thoracic spine are notoriously unreliable. For instance, one poll found that 4% of individuals had thoracic spine discomfort, while another found that 72% of people had the same problem.
It seems to be most frequent among kids and teens, particularly young women. The usage of backpacks, the height of school seats and the difficulty of schoolwork were all mentioned as potential causes of thoracic back discomfort.
Symptoms of Thoracic Back Pain
These are the warning signs to keep an eye out for if you’re experiencing thoracic back pain:
- Recent, severe injury from anything like a vehicle crash or a fall from a great height.
- People with ‘thinning of the bones are more prone to fractures from even little trauma or heavy lifting (osteoporosis).
- If you’re under 20 or over 50 when the pain begins, it’s likely that you’re in the older age group.
- Cancer, substance abuse, HIV infection, immunosuppression and long-term steroid use all lower the immune system’s ability to fight off disease (about six months or more).
Causes of Back Pain in the Thoracic Region
- Inflammation of the muscles or soft tissues of the thoracic spine is the most prevalent cause of thoracic back pain. Inflammation may arise for several reasons.
- The strain or sprain occurred all of a sudden (as in car accidents or sports injuries).
- Long-term slumping in one’s seat or posture.
- By use of a backpack.
- Long periods of time spent seated in front of a computer.
- Inability to build muscle (watch out, couch potatoes).
- Overuse injuries may occur from repetitive motions that stress the thoracic back, such as those performed in sports or on the job.
Diagnostic tests
The doctor’s decision to order tests is based on the diagnoses he or she hopes to rule out. In addition to a complete blood count and inflammatory marker blood test, an MRI scan may also be recommended. Unless there is anything out of the ordinary about the look of the spine or a fracture is suspected, a regular X-ray won’t reveal much.
Treatment
- There are numerous situations that resolve themselves without therapy.
- If there is a deeper issue at play, it has to be addressed apart from the symptomatology.
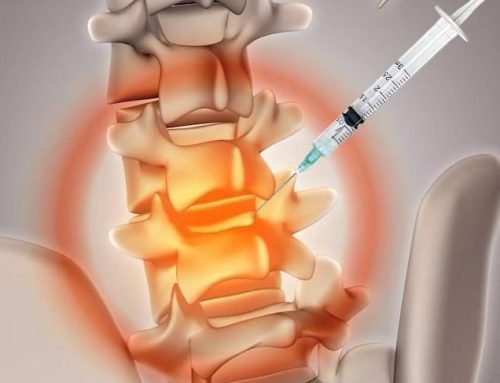
- An X-ray-guided injection may be helpful if the source of the pain is determined to be a joint in the spine (a facet joint) (imaging-guided intra-articular injection).
- There is some risk involved with undergoing laminectomy, a technique used to relieve thoracic spine discomfort caused by a slipped disc. However, there is an alternative procedure called percutaneous thoracic intervertebral disc nucleoplasty that is done when necessary since it involves less risk.
Conclusion
In case you are looking for Thoracic pain diagnostic tests or treatment, get in touch with Dr.Vikram Rajguru in Pune.